High myopia: over 8 dioptres
12 de April de 2022
How does high myopia affect eye health?
Patients with high myopia, who account for around 2% of the population, are more likely to suffer certain eye diseases such as glaucoma or cataracts and, more particularly, retina-related disorders such as retinal detachment, central retinal degeneration due to atrophic plaques, vessel growth in the macular area below the retina, myopic macular hole or separation of the macular retina layers, known as schisis.

The most common symptoms in myopia patients with retina problems are wavy lines or hazy spots in their field of vision and loss of visual acuity. In some cases, the lesions may go unnoticed until the patient undergoes a full ophthalmic check-up.
How can it be prevented?
The pathological elongation of the eyeball is the cause of retina problems in high myopia sufferers, as this is affected by the stretching or detachment of its layers.
Regular ophthalmic check-ups detect lesions to the retina that might otherwise go unnoticed.
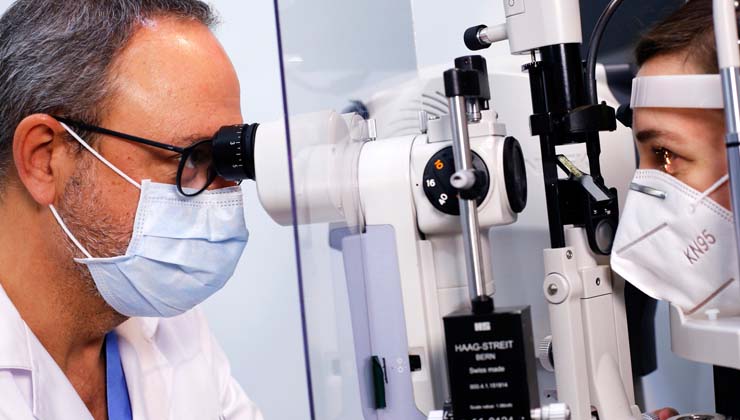

Ocular check up of retina
People with more than 8 dioptres have certain limitations to treatment, such as refractive surgery with Excimer laser, which is recommended for patients with less than 8 dioptres. There are techniques, however, such as intraocular lens implantation, which are a good option. This is weighed up in consultation and a decision is made as to the most suitable type of lens for each patient, for his/her cornea type, and his/her visual needs.
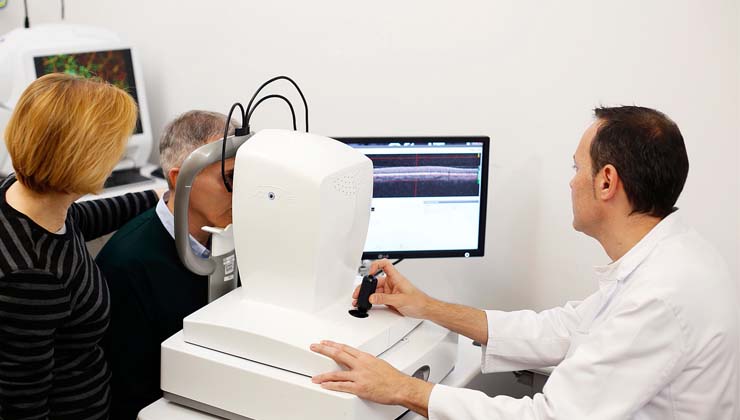

Regular ophthalmic check-ups detect lesions
How often should a hight myopic visit the ophthalmologist?
Myopia sufferers with more than 8 dioptres must undergo a full ophthalmic check-up at least once a year, or more often if your ophthalmologist recommends as such.
Visit your ophthalmologist urgently in the event of a sudden loss of visual acuity or the sudden appearance of wavy lines, flashes or hazy spots in your field of vision.
The prodromes to retinal detachment are sudden, severe floaters, continuous flashes, and ultimately major shadowing
Dr Carlos Mateo
Eye disorders associated to high myopia
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts
- Retinal detachment
- Myopic macular hole
- Degeneration of the central retina caused by atrophic patches
- Growth of blood vessels beneath the retina in the macular area
- Separation of the layers of the macular retina, known as schisis.
IMO Institute of Ocular Microsurgery
Josep María Lladó, 3
08035 Barcelona
Phone: (+34) 934 000 700
E-mail: international@imo.es
See map on Google Maps
By car
GPS navigator coordinates:
41º 24’ 38” N – 02º 07’ 29” E
Exit 7 of the Ronda de Dalt (mountain side). The clinic has a car park with more than 200 parking spaces.
By bus
Autobus H2: Rotonda de Bellesguard, parada 1540
Autobus 196: Josep Maria Lladó-Bellesguard, parada 3191
Autobuses H2, 123, 196: Ronda de Dalt – Bellesguard, parada 0071
How to arrive at IMO from:
IMO Madrid
C/ Valle de Pinares Llanos, 3
28035 Madrid
Phone: (+34) 910 783 783
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
Metro Lacoma (líne 7)
Autobuses:
- Lines 49 & 64, stop “Senda del Infante”
- Line N21, stop “Metro Lacoma”
Timetables
Patient care:
Monday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 9 p.m.
IMO Andorra
Av. de les Nacions Unides, 17
AD700 Escaldes-Engordany, Andorra
Phone: (+376) 688 55 44
See map in Google Maps
IMO Manresa
C/ Carrasco i Formiguera, 33 (Baixos)
08242 – Manresa
Tel: (+34) 938 749 160
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
FGC. Line R5 & R50 direction Manresa. Station/Stop: Baixador de Manresa
Timetables
Monday to Friday, 09:00 A.M – 07:00 PM