What does it involve?
Brachytherapy is radiotherapy treatment at close range. It involves placing a radioactive source in contact with the surface of the eyeball with ruthenium-106 or iodine-125, which are radioactive isotopes.
When is it carried out?
The treatment is used for malignant intraocular tumours, such as choroidal melanomas, retinoblastomas and intraocular metastasis. Brachytherapy can also be indicated for cases of vascular tumours, such as retinal capillary angiomas and cavernous angiomas.
Prior examination
In the case of choroidal melanoma treatment, it is very important to find out the condition of the liver, because, if metastasis occurs, 90% of cases affect the liver. Liver function is checked by means of tests and a liver ultrasound. A CT scan should also be carried out to detect for tumours throughout the body. The scan uses a contrast technique to detect for tumours that are larger than 5 mm.
Before the surgery
In the case of choroidal melanoma treatment, it is very important to perform a comprehensive examination of the condition of the liver.
Surgery
During the procedure, the conjunctiva is dissected and, by means of transillumination or marking systems while observing the fundus, the tumour can be precisely located and the radioactive ruthenium or iodine plaque, which is prepared exclusively for the patient, can be positioned. These plaques are covered by a layer of silver or gold to ensure that the radiation is applied to the interior of the eyeball, preventing it from spreading outwards. The plaque is implanted with a certain dose of radiation that lethally damages the tumour cells, which, over the following months, atrophy and leave tumour-free scar tissue.
Risks
There are no significant risks to take into account.
Associated pathologies
Experts performing this treatment
FAQs
Eye tumours can occur on any tissue, but the most common in adults is choroidal melanoma, a malignant tumour that can be treated with radiotherapy and other treatments with notable success. Malignant tumours can also appear on the conjunctiva, the lacrimal gland and the orbit. Benign tumours can also appear, but they can be easily dried out. In children a retinal tumour known as retinoblastoma can appear, which looks like a white pupil and must be treated as soon as possible, as it can be life-threatening if appropriate treatment is not performed.
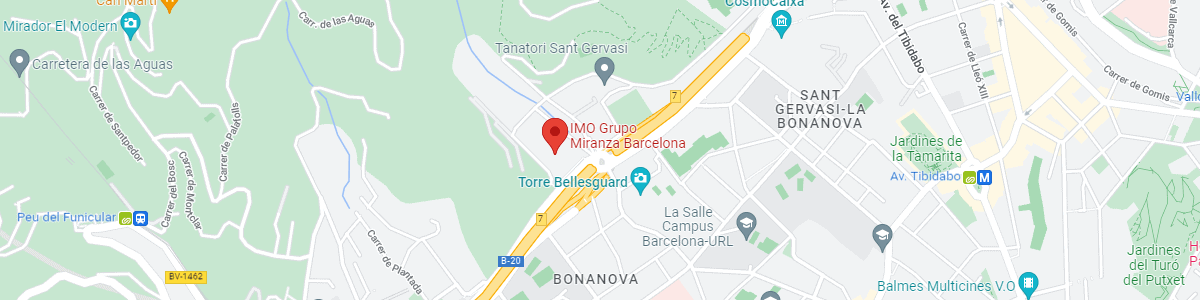
IMO Institute of Ocular Microsurgery
Josep María Lladó, 3
08035 Barcelona
Phone: (+34) 934 000 700
E-mail: international@imo.es
See map on Google Maps
By car
GPS navigator coordinates:
41º 24’ 38” N – 02º 07’ 29” E
Exit 7 of the Ronda de Dalt (mountain side). The clinic has a car park with more than 200 parking spaces.
By bus
Autobus H2: Rotonda de Bellesguard, parada 1540
Autobus 196: Josep Maria Lladó-Bellesguard, parada 3191
Autobuses H2, 123, 196: Ronda de Dalt – Bellesguard, parada 0071
How to arrive at IMO from:
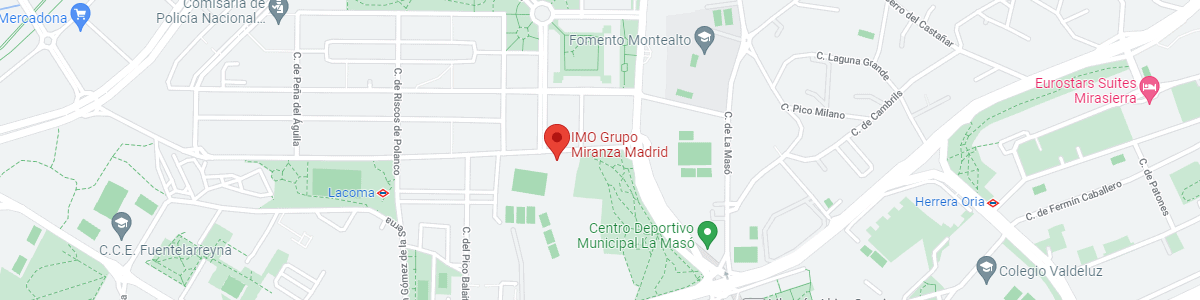
IMO Madrid
C/ Valle de Pinares Llanos, 3
28035 Madrid
Phone: (+34) 910 783 783
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
Metro Lacoma (líne 7)
Autobuses:
- Lines 49 & 64, stop “Senda del Infante”
- Line N21, stop “Metro Lacoma”
Timetables
Patient care:
Monday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 9 p.m.
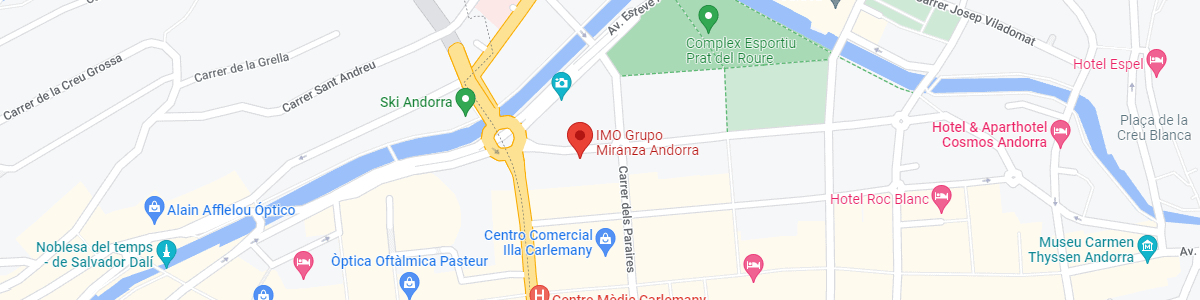
IMO Andorra
Av. de les Nacions Unides, 17
AD700 Escaldes-Engordany, Andorra
Phone: (+376) 688 55 44
See map in Google Maps
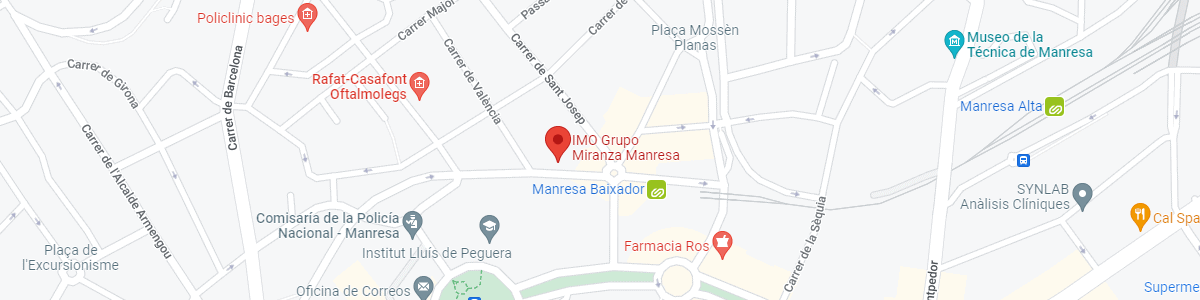
IMO Manresa
C/ Carrasco i Formiguera, 33 (Baixos)
08242 – Manresa
Tel: (+34) 938 749 160
See map in Google Maps
Public transport
FGC. Line R5 & R50 direction Manresa. Station/Stop: Baixador de Manresa
Timetables
Monday to Friday, 09:00 A.M – 07:00 PM